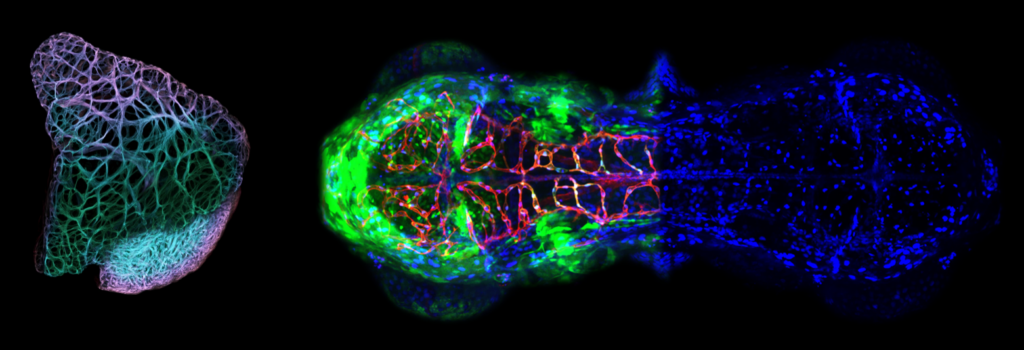
cardiovascular development and blood-brain barrier formation
Dysfunction of the inner lining of the blood vessels, called the endothelium, is the single most common cause of human disease and mortality. My research is focused on the formation and integrity of the cardiovascular system. By combining molecular techniques, such as transcriptional analysis and genetic manipulations, with imaging techniques in different model organisms and cells; we aim to broaden the understanding of endothelial barrier formation, revealing potential novel therapeutic targets.
2025
in review & preparation
Raoul F.V. Germano et al.
2024
A brain-specific angiogenic mechanism enabled by tip cell specialization
Giel Schevenels, Pauline Cabochette, Michelle America, Arnaud Vandenborne, Line De Grande, Stefan Guenther, Liqun He, Marc Dieu, Basile Christou, Marjorie Vermeersch, Raoul F. V. Germano, David Perez-Morga, Patricia Renard, Maud Martin, Michael Vanlandewijck, Christer Betsholtz & Benoit Vanhollebeke
Nature
Vertebrate organs require locally adapted blood vessels1,2. The gain of such organotypic vessel specializations is often deemed to be molecularly unrelated to the process of organ vascularization. Here, opposing this model, we reveal a molecular mechanism for brain-specific angiogenesis that operates under the control of Wnt7a/b ligands-well-known blood-brain barrier maturation signals3-5. The control mechanism relies on Wnt7a/b-dependent expression of Mmp25, which we find is enriched in brain endothelial cells. CRISPR-Cas9 mutagenesis in zebrafish reveals that this poorly characterized glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored matrix metalloproteinase is selectively required in endothelial tip cells to enable their initial migration across the pial basement membrane lining the brain surface. Mechanistically, Mmp25 confers brain invasive competence by cleaving meningeal fibroblast-derived collagen IV α5/6 chains within a short non-collagenous region of the central helical part of the heterotrimer. After genetic interference with the pial basement membrane composition, the Wnt-β-catenin-dependent organotypic control of brain angiogenesis is lost, resulting in properly patterned, yet blood-brain-barrier-defective cerebrovasculatures. We reveal an organ-specific angiogenesis mechanism, shed light on tip cell mechanistic angiodiversity and thereby illustrate how organs, by imposing local constraints on angiogenic tip cells, can select vessels matching their distinctive physiological requirements.
The cytoskeleton adaptor protein Sorbs1 controls the development of lymphatic and venous vessels in zebrafish
Alexandra Veloso, Anouk Bleuart, Louise Conrard, Tanguy Orban, Jonathan Bruyr, Pauline Cabochette, Raoul F. V. Germano, Giel Schevenels, Alice Bernard, Egor Zindy, Sofie Demeyer, Benoit Vanhollebeke, Franck Dequiedt & Maud Martin
BMC Biology
Background
Lymphangiogenesis, the formation of lymphatic vessels, is tightly linked to the development of the venous vasculature, both at the cellular and molecular levels. Here, we identify a novel role for Sorbs1, the founding member of the SoHo family of cytoskeleton adaptor proteins, in vascular and lymphatic development in the zebrafish.
Results
We show that Sorbs1 is required for secondary sprouting and emergence of several vascular structures specifically derived from the axial vein. Most notably, formation of the precursor parachordal lymphatic structures is affected in sorbs1 mutant embryos, severely impacting the establishment of the trunk lymphatic vessel network. Interestingly, we show that Sorbs1 interacts with the BMP pathway and could function outside of Vegfc signaling. Mechanistically, Sorbs1 controls FAK/Src signaling and subsequently impacts on the cytoskeleton processes regulated by Rac1 and RhoA GTPases. Inactivation of Sorbs1 altered cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) contacts rearrangement and cytoskeleton dynamics, leading to specific defects in endothelial cell migratory and adhesive properties.
Conclusions
Overall, using in vitro and in vivo assays, we identify Sorbs1 as an important regulator of venous and lymphatic angiogenesis independently of the Vegfc signaling axis. These results provide a better understanding of the complexity found within context-specific vascular and lymphatic development.
2022
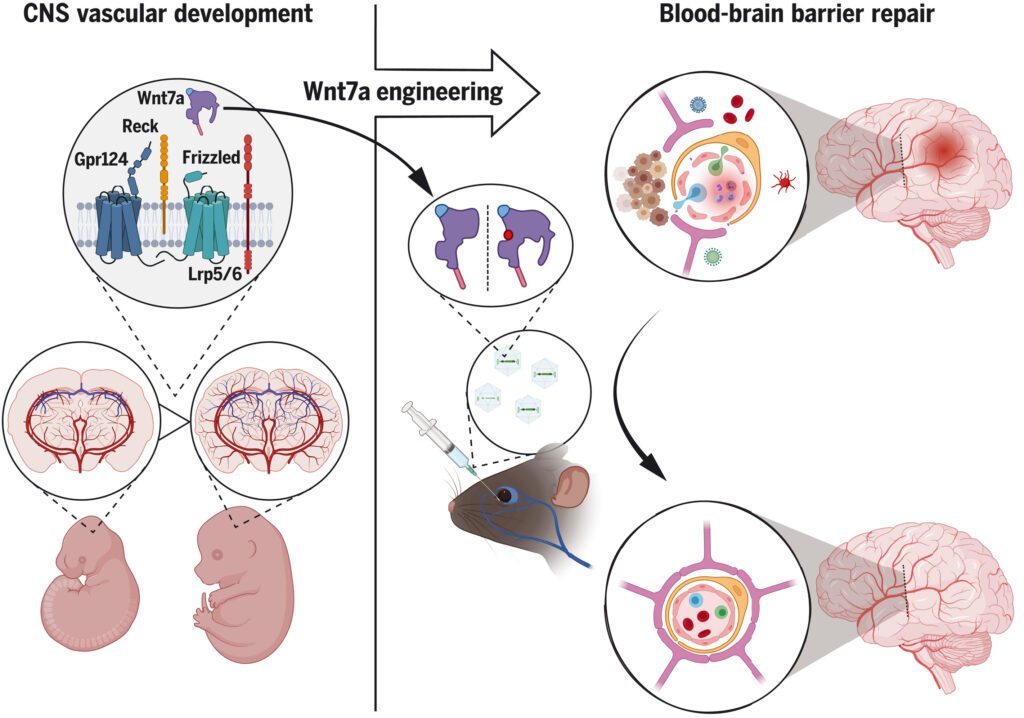
Engineered Wnt ligands enable blood-brain barrier repair in neurological disorders
Maud Martin, Simon Vermeiren, Naguissa Bostaille, Marie Eubelen, Daniel Spitzer, Marjorie Vermeersch, Caterina P Profaci, Elisa Pozuelo, Xavier Toussay, Joanna Raman-Nair, Patricia Tebabi, Michelle America, Aurélie De Groote, Leslie E Sanderson, Pauline Cabochette, Raoul F V Germano, David Torres, Sébastien Boutry, Alban de Kerchove d’Exaerde , Eric J Bellefroid, Timothy N Phoenix, Kavi Devraj, Baptiste Lacoste, Richard Daneman, Stefan Liebner, Benoit Vanhollebeke
Science
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) protects the central nervous system (CNS) from harmful blood-borne factors. Although BBB dysfunction is a hallmark of several neurological disorders, therapies to restore BBB function are lacking. An attractive strategy is to repurpose developmental BBB regulators, such as Wnt7a, into BBB-protective agents. However, safe therapeutic use of Wnt ligands is complicated by their pleiotropic Frizzled signaling activities. Taking advantage of the Wnt7a/b-specific Gpr124/Reck co-receptor complex, we genetically engineered Wnt7a ligands into BBB-specific Wnt activators. In a “hit-and-run” adeno-associated virus-assisted CNS gene delivery setting, these new Gpr124/Reck-specific agonists protected BBB function, thereby mitigating glioblastoma expansion and ischemic stroke infarction. This work reveals that the signaling specificity of Wnt ligands is adjustable and defines a modality to treat CNS disorders by normalizing the BBB.
2020
Advancing brain barriers RNA sequencing: guidelines from experimental design to publication
David M F Francisco, Luca Marchetti, Sabela Rodríguez-Lorenzo, Eduardo Frías-Anaya, Ricardo M Figueiredo; BtRAIN Network; Peter Winter , Ignacio Andres Romero, Helga E de Vries, Britta Engelhardt, Rémy Bruggmann
Fluids Barrier of the CNS
Background: RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) in its varied forms has become an indispensable tool for analyzing differential gene expression and thus characterization of specific tissues. Aiming to understand the brain barriers genetic signature, RNA seq has also been introduced in brain barriers research. This has led to availability of both, bulk and single-cell RNA-Seq datasets over the last few years. If appropriately performed, the RNA-Seq studies provide powerful datasets that allow for significant deepening of knowledge on the molecular mechanisms that establish the brain barriers. However, RNA-Seq studies comprise complex workflows that require to consider many options and variables before, during and after the proper sequencing process.
Main body: In the current manuscript, we build on the interdisciplinary experience of the European PhD Training Network BtRAIN ( https://www.btrain-2020.eu/ ) where bioinformaticians and brain barriers researchers collaborated to analyze and establish RNA-Seq datasets on vertebrate brain barriers. The obstacles BtRAIN has identified in this process have been integrated into the present manuscript. It provides guidelines along the entire workflow of brain barriers RNA-Seq studies starting from the overall experimental design to interpretation of results. Focusing on the vertebrate endothelial blood-brain barrier (BBB) and epithelial blood-cerebrospinal-fluid barrier (BCSFB) of the choroid plexus, we provide a step-by-step description of the workflow, highlighting the decisions to be made at each step of the workflow and explaining the strengths and weaknesses of individual choices made. Finally, we propose recommendations for accurate data interpretation and on the information to be included into a publication to ensure appropriate accessibility of the data and reproducibility of the observations by the scientific community.
Conclusion: Next generation transcriptomic profiling of the brain barriers provides a novel resource for understanding the development, function and pathology of these barrier cells, which is essential for understanding CNS homeostasis and disease. Continuous advancement and sophistication of RNA-Seq will require interdisciplinary approaches between brain barrier researchers and bioinformaticians as successfully performed in BtRAIN. The present guidelines are built on the BtRAIN interdisciplinary experience and aim to facilitate collaboration of brain barriers researchers with bioinformaticians to advance RNA-Seq study design in the brain barriers community.
2019
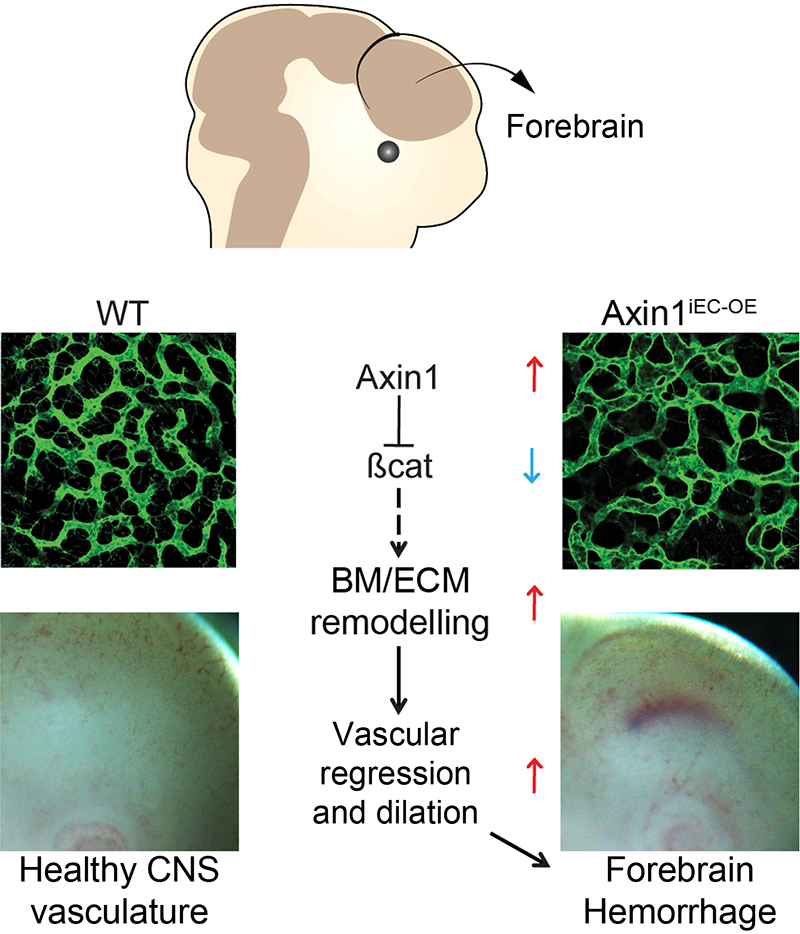
Disruption of the Extracellular Matrix Progressively Impairs Central Nervous System Vascular Maturation Downstream of β-Catenin Signaling
Lasse D. Jensen, Belma Hot, Daniel Ramsköld, Raoul F.V. Germano, Chika Yokota, Sarantis Giatrellis, Volker M. Lauschke, …, and Julianna Kele
Atherosclerosis trombosis and vascular biology
Objective- The Wnt/β-catenin pathway orchestrates development of the blood-brain barrier, but the downstream mechanisms involved at different developmental windows and in different central nervous system (CNS) tissues have remained elusive. Approach and Results- Here, we create a new mouse model allowing spatiotemporal investigations of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by induced overexpression of Axin1, an inhibitor of β-catenin signaling, specifically in endothelial cells ( Axin1 iEC– OE). AOE (Axin1 overexpression) in Axin1 iEC– OE mice at stages following the initial vascular invasion of the CNS did not impair angiogenesis but led to premature vascular regression followed by progressive dilation and inhibition of vascular maturation resulting in forebrain-specific hemorrhage 4 days post-AOE. Analysis of the temporal Wnt/β-catenin driven CNS vascular development in zebrafish also suggested that Axin1 iEC– OE led to CNS vascular regression and impaired maturation but not inhibition of ongoing angiogenesis within the CNS. Transcriptomic profiling of isolated, β-catenin signaling-deficient endothelial cells during early blood-brain barrier-development (E11.5) revealed ECM (extracellular matrix) proteins as one of the most severely deregulated clusters. Among the 20 genes constituting the forebrain endothelial cell-specific response signature, 8 ( Adamtsl2, Apod, Ctsw, Htra3, Pglyrp1, Spock2, Ttyh2, and Wfdc1) encoded bona fide ECM proteins. This specific β-catenin-responsive ECM signature was also repressed in Axin1 iEC– OE and endothelial cell-specific β-catenin-knockout mice ( Ctnnb1-KOiEC) during initial blood-brain barrier maturation (E14.5), consistent with an important role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in orchestrating the development of the forebrain vascular ECM. Conclusions- These results suggest a novel mechanism of establishing a CNS endothelium-specific ECM signature downstream of Wnt-β-catenin that impact spatiotemporally on blood-brain barrier differentiation during forebrain vessel development.
Low wnt/β-catenin signaling determines leaky vessels in the subfornical organ and affects water homeostasis in mice
Fabienne Benz, Viraya Wichitnaowarat, Martin Lehmann, Raoul Fv Germano, Diana Mihova, Jadranka Macas, Ralf H Adams, M Mark Taketo, Karl-Heinz Plate, Sylvaine Guérit, Benoit Vanhollebeke , Stefan Liebner
Elife 2019
The circumventricular organs (CVOs) in the central nervous system (CNS) lack a vascular blood-brain barrier (BBB), creating communication sites for sensory or secretory neurons, involved in body homeostasis. Wnt/β-catenin signaling is essential for BBB development and maintenance in endothelial cells (ECs) in most CNS vessels. Here we show that in mouse development, as well as in adult mouse and zebrafish, CVO ECs rendered Wnt-reporter negative, suggesting low level pathway activity. Characterization of the subfornical organ (SFO) vasculature revealed heterogenous claudin-5 (Cldn5) and Plvap/Meca32 expression indicative for tight and leaky vessels, respectively. Dominant, EC-specific β-catenin transcription in mice, converted phenotypically leaky into BBB-like vessels, by augmenting Cldn5+vessels, stabilizing junctions and by reducing Plvap/Meca32+ and fenestrated vessels, resulting in decreased tracer permeability. Endothelial tightening augmented neuronal activity in the SFO of water restricted mice. Hence, regulating the SFO vessel barrier may influence neuronal function in the context of water homeostasis.
2018
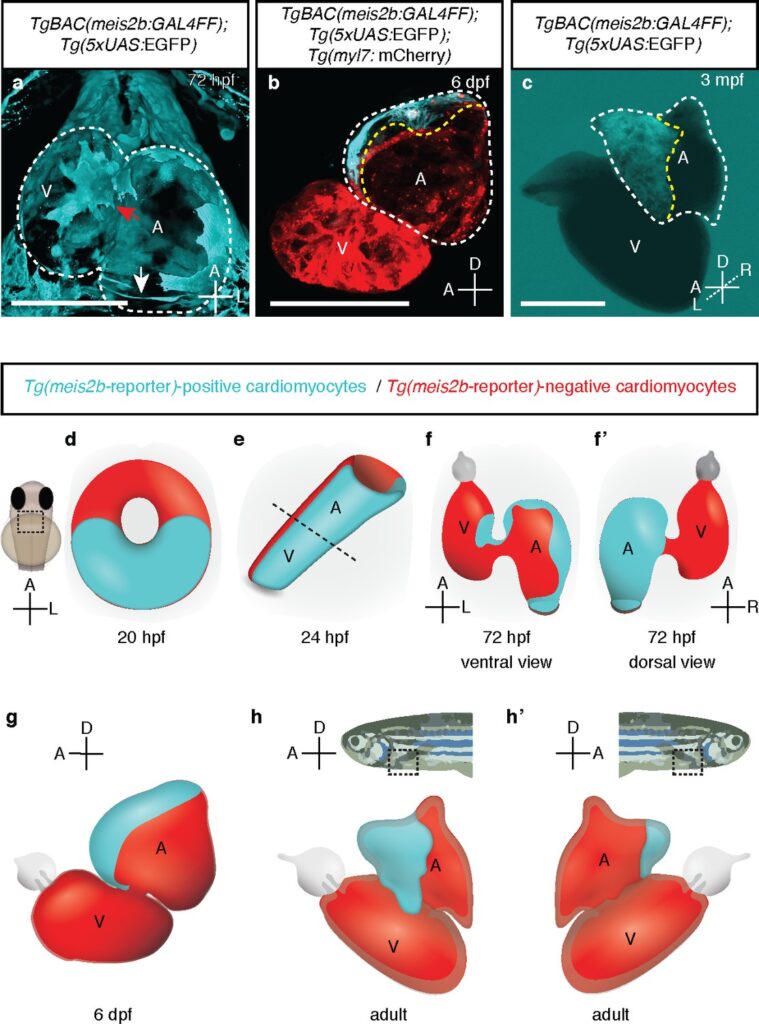
Distinct myocardial lineages break atrial symmetry during cardiogenesis in zebrafish
Almary Guerrra and Raoul F.V. Germano*, Oliver Stone , Rima Arnaout, Stefan Guenther, Suchit Ahuja, Verónica Uribe, Benoit Vanhollebeke, Didier Yr Stainier, Sven Reischauer * equal contribution
Elife 2018
The ultimate formation of a four-chambered heart allowing the separation of the pulmonary and systemic circuits was key for the evolutionary success of tetrapods. Complex processes of cell diversification and tissue morphogenesis allow the left and right cardiac compartments to become distinct but remain poorly understood. Here, we describe an unexpected laterality in the single zebrafish atrium analogous to that of the two atria in amniotes, including mammals. This laterality appears to derive from an embryonic antero-posterior asymmetry revealed by the expression of the transcription factor gene meis2b. In adult zebrafish hearts, meis2b expression is restricted to the left side of the atrium where it controls the expression of pitx2c, a regulator of left atrial identity in mammals. Altogether, our studies suggest that the multi-chambered atrium in amniotes arose from a molecular blueprint present before the evolutionary emergence of cardiac septation and provide insights into the establishment of atrial asymmetry.
awards & grants
2021 European Research Councel (ERC) (GoGCtrl-BBB 865176)
2020-2021 Jean et Rose Hoguet Fellowship
2016-2019 Marie-SkolodowskaCuriefellowship, BtRAIN
2013 SFB-grant German Research Foundation
2012 PhD Scholarship, MaxPlanck Society
2011 Dutch Talent GrantNuffic: ʻHuygensScholarship Program
2011 Personal grant and excellence award, Dutch HeartAssociation, ʻDr. Eduard Dekker programʼ
2009 Student-grant, Dutch Brain Association
2009 Spinoza-award, University of Amsterdam